White-eyed Thrush Turdus jamaicensis Scientific name definitions
- LC Least Concern
- Names (18)
- Monotypic
Text last updated January 10, 2015
Sign in to see your badges
Species names in all available languages
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Catalan | merla de Jamaica |
| Dutch | Witooglijster |
| English | White-eyed Thrush |
| English (United States) | White-eyed Thrush |
| French | Merle aux yeux blancs |
| French (France) | Merle aux yeux blancs |
| German | Weißaugendrossel |
| Japanese | メジロムジツグミ |
| Norwegian | hvitøyetrost |
| Polish | drozd białooki |
| Russian | Белоглазый дрозд |
| Serbian | Jamajkanski šareni kos |
| Slovak | drozd jamajský |
| Spanish | Zorzal Jamaicano |
| Spanish (Spain) | Zorzal jamaicano |
| Swedish | vitögd trast |
| Turkish | Ak Gözlü Ardıç |
| Ukrainian | Дрізд білоокий |
Turdus jamaicensis Gmelin, 1789
Definitions
- TURDUS
- turdus
- jamaica / jamaicae / jamaicana / jamaicensis
The Key to Scientific Names
Legend Overview
Introduction
The White-eyed Thrush is a common and distinctive thrush of montane and lowland forests and disturbed areas on the island of Jamaica. The body is gray overall, with darker upperparts than underparts. The head is chocolate brown, and the throat has white streaks on a brown background, bordered below by a white patch. The eye is white.
Field Identification
23–24 cm; 59 g. Plumage is slate-grey from mantle to tail, pale grey-brown below ; dark chestnut-brown head , white eye ; white chin and throat streaked chestnut-brown, joining small white crescent on upper breast, white vent ; bill and legs blackish. Sexes similar. Juvenile is like adult, but with heavy breast streaking.
Systematics History
Subspecies
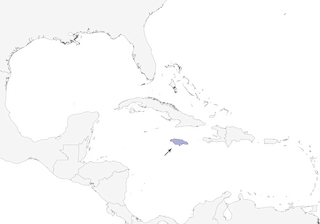
Distribution
Jamaica.
Habitat
Movement
Diet and Foraging
Sounds and Vocal Behavior
Song a series of repeated, musical phrases, including whistled “hee-haw”, resembling that of Northern Mockingbird (Mimus polyglottos) but louder and less variable. Calls harsh and shrill.
Breeding
Conservation Status
- Year-round
- Migration
- Breeding
- Non-Breeding



























